From Copilot to Goal-Oriented Agents: Navigating the Challenges of Coordination and Shared Context
The evolution of AI from being a simple assistant to a goal-oriented agent capable of making autonomous decisions is a transformative shift for businesses. While AI copilot tools have been popular for assisting individuals in performing tasks, organisations are increasingly focusing on designing intelligent agents that can work seamlessly across entire business processes. However, as we move towards this next generation of AI, the real challenge lies in coordination and ensuring shared context to drive meaningful iterations and results.
In this article, we will explore the journey from AI as a copilot to goal-oriented agents and the complexities of creating intelligent, autonomous agents that can collaborate effectively within business processes unlocking greater efficiencies across organisations.
The Evolution of AI: From Copilot to Goal-Oriented Agents
In the early stages, AI was designed primarily as a copilot – tools that supported human actions but did not drive processes independently. Think of these as chatbots or digital assistants, helping with tasks but always requiring human input for direction. While these AI copilots were a valuable addition to workflows, their limitations became apparent as organisations demanded more robust and scalable solutions.
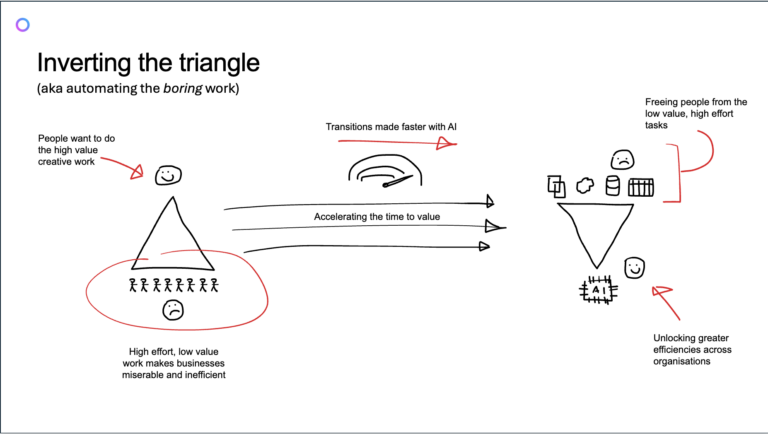
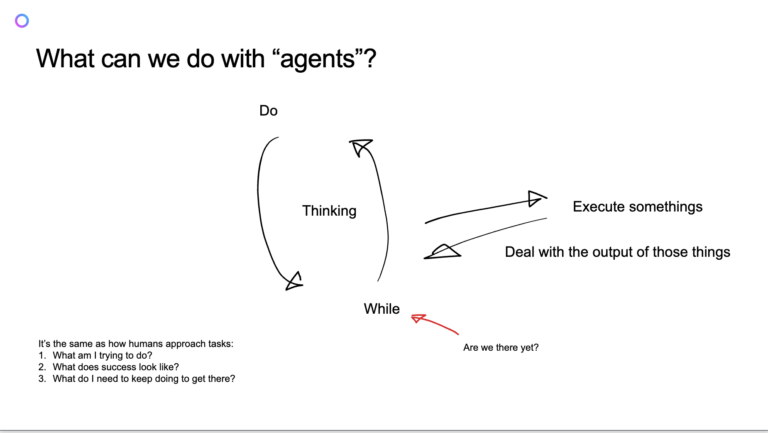
Now, we’re witnessing the emergence of AI agents that are goal-oriented – AI systems that don’t just assist but also drive actions towards achieving specific business outcomes. These agents are designed to autonomously follow a defined process, make decisions based on input data, and run at their own pace. However, as AI systems become more independent, they must be given clear goals to avoid becoming “lazy” or disengaged, like an AI agent sitting in a garden drinking beer and eating burgers, with no task at hand. The key challenge, therefore, is not only creating autonomous agents but ensuring that these agents are equipped with goals that align with business processes.
Coordination and Shared Context: The Key Challenges in Iteration
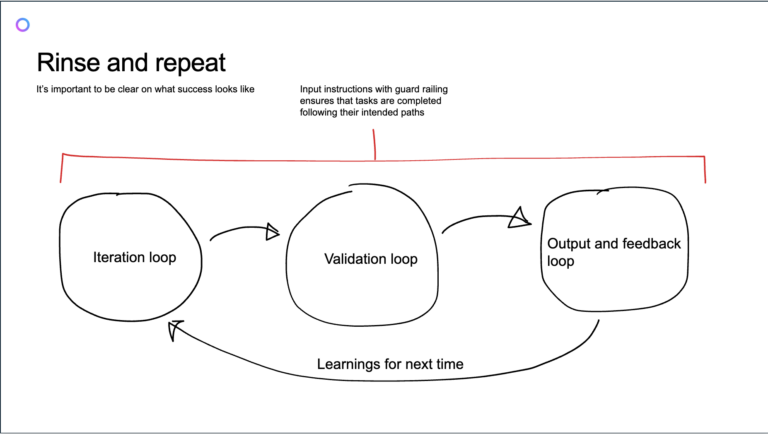
The concept of goal-oriented agents requires effective coordination among various AI systems, each working towards different sub-tasks in a larger process. This coordination is essential for ensuring that agents not only work autonomously but also maintain a shared understanding of context to improve their decision-making abilities over time. To address this challenge, business processes need to be systematically integrated with AI. This integration isn’t about removing human input but about making people more efficient. Agents need to be able to experiment with different solutions, quickly validating results and making adjustments in real time. For example, consider the early days of Web 2.0, where services like “If this, then that” allowed users to automate simple workflows based on predefined triggers. This idea of experimentation and iteration is now central to AI’s evolution into a goal-oriented agent. However, as agents become more complex, there are new hurdles. Defining the instructions for these agents can be difficult, especially when those responsible for creating these systems are not always technology experts. The ability to teach AI systems the intricacies of specific business tasks – whether it’s an HR workflow, sales prospecting, or content creation – requires a thoughtful approach to creating clear, reproducible steps that an AI can follow. Without these instructions, even the most advanced AI may fail to meet expectations.
The Balance Between Monolithic and Microservices Approaches
As businesses develop their AI strategies, a key decision point arises: should they opt for a monolithic AI architecture or a more granular, microservices-based approach? Both approaches have their pros and cons, and the choice largely depends on the scale of the business and the specific needs of the workflow.A monolithic AI system is akin to a single, unified solution that handles all tasks within a specific business process. For example, a monolithic HR agent could manage multiple HR tools and processes within one system. While this approach is easier to deploy and maintain, it also presents a risk: if one part of the system fails, the entire process could break down.
On the other hand, a microservices approach involves breaking down the process into smaller, more specialised AI agents that each focus on specific tasks. For instance, at Firemind, we use specialised agents for Salesforce, Confluence, and even web surfing. These agents collaborate as part of a larger system, but they each operate independently, meaning that if one agent fails, the overall process can still continue. While this approach offers greater flexibility and resilience, it also introduces complexities in managing multiple agents and ensuring they communicate effectively.The trade-off between these two approaches is significant. Monolithic systems offer simplicity but may not be adaptable to the diverse needs of all customers. Microservices, while flexible, can increase the complexity of the overall system, requiring more maintenance and coordination among agents.
The Future: Collaborative AI Agents
Looking ahead, the real potential of AI lies in creating agents that not only work autonomously but collaborate with other agents in a shared context. These collaborative agents can help businesses tackle complex problems that require input from multiple sources or perspectives.
Imagine an AI that combines sales prospecting with customer support, using real-time data from various departments to make decisions and act on opportunities immediately. This collaboration is the next frontier in AI, moving beyond individual agents working in silos to create a more integrated system where agents can support and learn from each other. The key challenge in this space is ensuring that each agent has access to the same shared context and is able to iterate based on real-time data and feedback from other agents. At Firemind, we are already developing systems like Pulse, an orchestrator that manages workflows and coordinates the work of multiple specialised agents. Pulse doesn’t act like an agent on its own; instead, it uses other agents to complete tasks, whether that’s accessing Salesforce, navigating the web, or managing content. By combining these specialised agents into a cohesive process, Pulse helps businesses streamline their operations while maintaining flexibility.
Conclusion: Building the Future of Goal-Oriented AI Agents
The shift from AI copilots to goal-oriented agents is not just a technological advancement; it represents a fundamental change in how businesses can approach automation and process improvement. The key to success in this transition lies in creating agents that not only act autonomously but collaborate effectively, with a clear understanding of shared context and the ability to iterate quickly. By addressing the challenges of coordination and process design, businesses can unlock the full potential of AI, driving efficiency and innovation across their operations.As we continue to develop AI systems that act as true goal-oriented agents, the focus must remain on ensuring that these agents are easy to design, integrate, and manage. The real power of AI comes not from its ability to operate in isolation but from its capacity to work collaboratively with people and other systems.For businesses ready to embark on this journey, Firemind’s Pulse platform offers a way to start integrating goal-oriented agents into your business processes. Start your AI journey today and explore how Pulse can help you unlock the potential of collaborative AI.
Watch Firemind CTO Ahmed Nuaman’s session on ‘Building the Right Foundations for Agentic AI below.
Watch Firemind CTO Ahmed Nuaman’s session on ‘Building the Right Foundations for Agentic AI below
Get the case study
Watch Firemind CTO Ahmed Nuaman’s session on ‘Building the Right Foundations for Agentic AI below
More client stories on agents
Get the full Bank of Ireland Case study
From inception to production, find out how the firemind team helped achieve and average of 20% time savings on routine tasks.